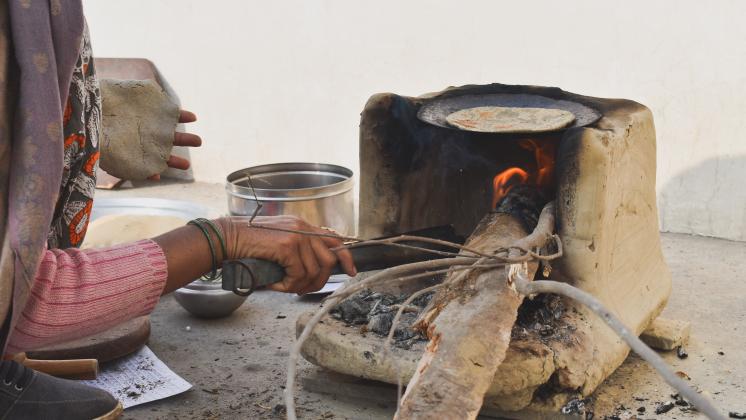
In much of the developing world, cooking accounts for the largest share of women’s time in home production. Does relying on solid fuels drive this time burden? This study revisits a clean energy information experiment in rural India to assess the time savings’ potential of cleaner cooking technologies. Treatment villages were randomly assigned to receive information about negative health effects of cooking with solid fuels and about public subsidies for cleaner liquid petroleum gas (LPG). Time-use data indicate that primary cooks spend almost 24 hours cooking each week. Cleaner fuel use is correlated with about 140 minutes less cooking time each week. Yet households only reduce their weekly cooking time by about 35 minutes in response to the randomized clean energy information nudge. Factors limiting the impact of clean energy nudges on the choice of home production technologies and time use are discussed and an avenue for future research is suggested.
Journal Article
• Research Theme 2: Labour, Home Production, and Structural Transformation at the Level of the Household,
Cross-Cutting Issue 1: Gender,
Cross-Cutting Issue 2: Climate Change and the Environment
Time for Clean Energy? Cleaner Fuels and Women’s Time in Home Production
Published in The World Bank Economic Review.

Related content